Wound Care 101: Understanding the Basics of Wound Management
Proper wound care is essential for promoting healing, preventing infections, and ensuring overall well-being. Whether it’s a minor cut or a more severe injury, understanding wound management can make a significant difference in recovery time and outcomes. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the basics of wound care for beginners, covering the types of wounds, treatment options, and best practices.
What Is Wound Care?
Wound care involves the assessment and treatment of injuries that break the skin or tissue, ranging from minor abrasions to deep surgical incisions. Effective wound care aims to:
- Promote faster healing.
- Prevent infections.
- Minimize scarring.
Types of Wounds
Understanding the type of wound is the first step in effective management. Common types include:
- Abrasions:
- Superficial wounds caused by friction, such as scrapes.
Lacerations:
- Deep cuts or tears in the skin, often caused by sharp objects.
Punctures:
- Small, deep holes made by pointed objects like nails or needles.
Burns:
- Caused by heat, chemicals, or radiation, burns can range from mild to severe.
Surgical Wounds:
- Incisions made during medical procedures.
Chronic Wounds:
- Long-lasting wounds like ulcers, often associated with underlying health conditions.
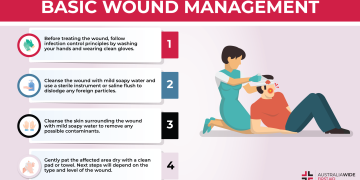
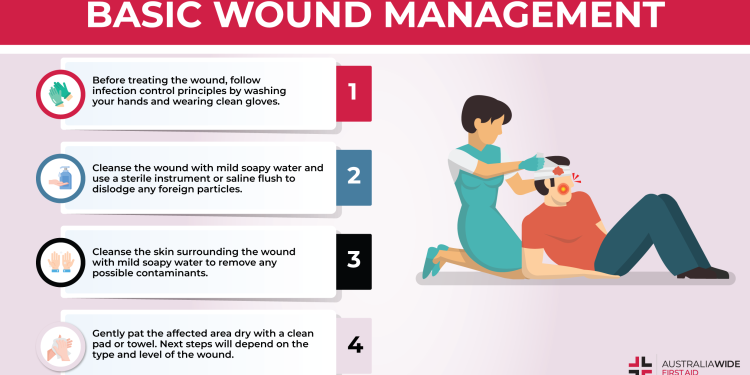
Basic Steps in Wound Care
- Assess the Wound:
- Examine the size, depth, and type of wound.
- Look for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge.
Clean the Wound:
- Use clean water or saline solution to rinse away dirt and debris.
- Avoid using harsh antiseptics like hydrogen peroxide, which can damage healthy tissue.
Stop Bleeding:
- Apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth or bandage.
- Elevate the wound above heart level if possible.
Apply a Dressing:
- Use a sterile bandage or dressing to cover the wound.
- For minor wounds, adhesive bandages may suffice; for larger wounds, opt for gauze and medical tape.
Monitor and Change Dressings:
- Replace the dressing regularly, especially if it becomes wet or dirty.
- Observe the wound for signs of infection or delayed healing.
Tips for Effective Wound Management
- Keep the Wound Moist:
- A moist environment promotes faster healing and reduces scarring.
- Use ointments or specialized dressings to maintain moisture.
Protect from Infection:
- Wash your hands before and after touching the wound.
- Avoid exposing the wound to unclean environments.
Maintain Good Nutrition:
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins C and A, zinc, and protein supports tissue repair.
Stay Hydrated:
- Proper hydration is crucial for overall healing and skin health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Certain wounds require professional care to ensure proper healing:
- Deep or Large Wounds:
- Injuries that expose muscles, tendons, or bones.
- Infected Wounds:
- Signs include pus, increasing pain, fever, or red streaks around the wound.
- Chronic Wounds:
- Wounds that do not show signs of healing after two weeks.
- Animal or Human Bites:
- These carry a higher risk of infection and may require antibiotics.
Common Wound Care Products
- Antiseptic Solutions:
- For cleaning wounds and preventing infections.
Adhesive Bandages:
- Suitable for small cuts and abrasions.
Hydrocolloid Dressings:
- Provide a moist environment for faster healing.
Antibiotic Ointments:
- Help prevent bacterial infections.
Compression Bandages:
- Useful for controlling swelling in larger wounds.
Understanding the basics of wound care is crucial for managing injuries effectively and preventing complications. By following proper wound management practices and knowing when to seek medical help, you can ensure a smoother recovery process. Whether it’s a minor cut or a chronic wound, taking proactive steps in care will promote healing and overall health. Remember, consistent care and attention to detail are the keys to optimal wound recovery. Take care of your elderly relatives and search for adult diapers if they are needed.
Homes for elderly always have this kind of product. It is important for the patients.